What is a Queue?
A line or sequence of people or vehicles awaiting their turn to be attended to or to proceed. This is the general description of a Queue. Similarly, when we consider Queue in data structures it is a collection of entities that are maintained in a sequence and can be modified by the addition of entities at one end of the sequence and the removal of entities from the other end of the sequence.
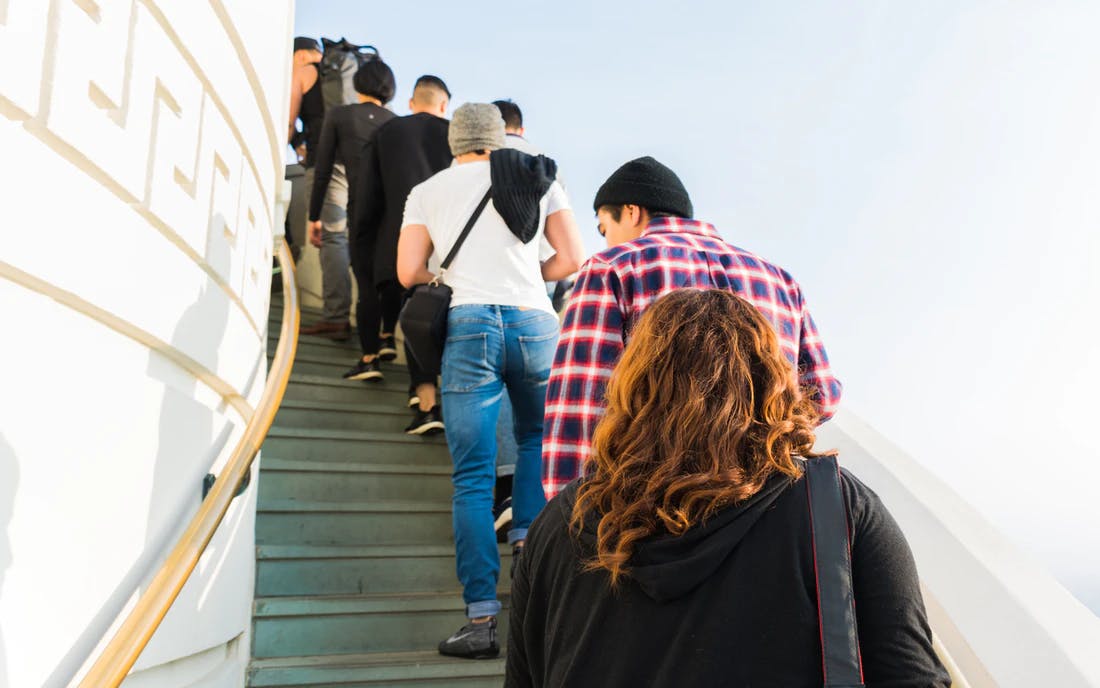
This represents Queue in real life, while you are standing in a line for buying a movie ticket for Wonder Women. The First-person standing in the line will get the ticket first and leave first, and the person joined the line at the moment will get the ticket last and will exit the queue last. This is known as FIFO which means First in - First out

In Python, we make use of the below Class for implementing Queue

Implementing Queue
- For Implementing a Queue in Python we will make use of List First
price = []
price.insert(0,100) # whenever we insert element at 0th position the older element is pushed forward
price.insert(0,200)
price.insert(0,300)
print(price)
# output will be [300,200,100]
- So what will happen when we use POP operation. As we know it will be FIFO - First in - First out . So the first element that was inserted will pop out first.
price = []
price.insert(0,100)
price.insert(0,200)
price.insert(0,300)
print(price.pop())
# output will be 100
- Though a List (Array) works fine for implementing a Queue but the problem will emerge due to Dynamic Array. When you are inserting in a Dynamic Array, first it will allocate random continues memory location and when its gets filled it will again allocate double the size of the memory location and then it will copy all old elements to the new location. Hence they are not recommended
Using Deque
A double-ended queue, or deque, has the feature of adding and removing elements from either end. The Deque module is a part of the collections library. It has the methods for adding and removing elements that can be invoked directly with arguments. In the below program we import the collections module and declare a deque. Without the need of any class, we use the in-built implement methods directly.
- Importing Deque form the Collection Library
from collections import deque
queue = deque()
- Since in the case of Queue we always add elements to the left side of the list so we will use the function appendleft()
from collections import deque
queue = deque()
queue.appendleft(100)
queue.appendleft(200)
queue.appendleft(300)
Now when we do a queue.pop() the value it will return will be 100 , because it was the first value that was inserted into the queue
Let's implement all these functions using a class QUEUE in Python
from collections import deque
class Queue:
def __init__(self):
self.queue = deque()
def insert(self,value):
self.value = value
self.queue.appendleft(value)
print(self.queue)
def delete(self):
self.queue.pop()
print(self.queue)
def length(self):
if len(self.queue)==0:
print("Empty")
else:
print(len(self.queue))
if __name__ =='__main__':
q = Queue()
q.insert(100)
q.insert(200)
q.delete()
q.length()
# OUTPUT will be
# deque([100])
# deque([200, 100])
# deque([200])
# 1
Thank-you!
I am glad you made it to the end of this article. I hope you got to learn something, if so please leave a Like which will encourage me for my upcoming write-ups.
- My GitHub Repos
- Connect with me on Linkedin
- Start your own blogs