| Feature | Linear Data Structures | Non-Linear Data Structures |
| Definition | Data elements are arranged in a sequence. | Data elements are arranged in a hierarchical manner. |
| Examples | Arrays, Linked Lists, Stacks, Queues | Trees, Graphs |
What are Arrays?
An array is a data structure that contains a group of elements, typically all of the same data type, such as integers or strings.
In Python, a list is implemented as a dynamic array. In other languages like Java and C++, both static arrays (with a fixed size) and dynamic arrays (which can change size) are used.
Advantages of Arrays:
Fast Access:
- Arrays allow direct access to elements using an index, which makes retrieving and modifying elements very fast (O(1) time complexity).
Efficient Memory Usage:
- Arrays store elements in contiguous memory locations, which can lead to efficient use of memory and faster access compared to other data structures like linked lists.
Easy to Traverse:
- Arrays are easy to traverse using simple loops, making them straightforward to work with for various algorithms.
Fixed Size:
- The size of an array is fixed when it is created, which can prevent unexpected memory usage increases during runtime.
Cache Friendliness:
- Due to their contiguous memory allocation, arrays are more cache-friendly, leading to better performance in terms of memory access speed.
Disadvantages of Arrays:
Fixed Size (for static arrays):
- Once the size of an array is set, it cannot be changed. This can lead to wasted memory if the array is not fully utilized, or insufficient space if more elements are needed.
Insertion and Deletion:
- Inserting or deleting elements in an array can be costly, especially if these operations occur at the beginning or in the middle of the array, as it requires shifting elements (O(n) time complexity).
Wasted Memory (for static arrays):
- If the allocated array size is larger than needed, memory is wasted. Conversely, if the array is too small, it might need to be resized or replaced, which can be inefficient.
No Built-in Dynamic Size Adjustment:
- In languages with static arrays, you need to manage resizing manually or use other data structures if you need dynamic resizing, which can add complexity.
Homogeneity:
- Arrays typically require that all elements be of the same data type, limiting flexibility if you need to store multiple data types.
Call by Value
Memory Allocation: In call by value, when you pass an array or any variable to a function, a copy of the data is made. Each copy of the data is stored in its own memory location. Changes made to the copy inside the function do not affect the original data.
Example: If you have an array and you pass it to a function using call by value, the function gets its own copy of the array data.
Original Array: 1[100], 2[104], 3[108] (where numbers in brackets are memory locations)If you modify this array inside the function, the original array remains unchanged, and only the copy is affected.
Call by Reference
Memory Allocation: In call by reference, you pass a reference (or pointer) to the actual data instead of a copy. This means that the function works directly with the original data, and changes made inside the function affect the original data.
Example: If you pass an array by reference, the function operates on the actual memory locations of the array elements.
Array: 1[102], 2[110], 3[409] (where numbers in brackets are memory locations) Reference Array: 102, 110, 409If you add a new element or modify the array, these changes will be reflected in the original array since the function has access to the actual memory locations.
Types of Arrays
Static Array
In the case of a static array, the size of the array is fixed at the time of its creation. For example, if you create an array with a capacity of 5 elements, you cannot add more than 5 elements to it. If you try to add more, in many languages, it will result in an error such as an Array Index Out of Bounds exception. However, this terminology should be corrected—“Array Index Out of Order” is not the correct term.
Dynamic Array
In contrast, a dynamic array does not require you to specify a fixed size upfront. You can keep adding elements, and the array will resize itself automatically to accommodate new elements.
How does a Dynamic Array work? When you insert elements into a dynamic array:
Initial Allocation: Initially, a dynamic array allocates a certain amount of memory (e.g., 10 blocks).
Capacity Doubling: When the array reaches its current capacity (e.g., you try to insert the 11th element in a 10-block array), the array will allocate a new memory block, typically doubling the previous size (so from 10 blocks, it becomes 20 blocks).
Element Copying: All elements from the original array are then copied to the new, larger memory block. After this, the new element is added to the array.
Further Resizing: This process repeats as more elements are added. For example, when you add the 21st element, the array's capacity may double again from 20 to 40 blocks. The final capacity after resizing is the new block size (e.g., 40 blocks), not a sum of the old and new sizes.
How are arrays stored in memory?
Let's take an example. Remember that the Indexing of array starts at 0.
scores = [30,40,50,60]
print(scores[2])
#the value will be 30 because the indexing starts from 0
We know that our computer only communicates using 0 and 1 . so lets assume we want to store 30 in some memory locations so first 30 will be converted to binary30 = 00011110 in binary
Now we store integers in 4 bytes which is the capacity of integers in most programming languages hence 30 will be stored like
30 = 00000000 00000000 00000000 00011110
#because (1 byte = 8 bits)
Now the integer 30 will be stored in the memory like -
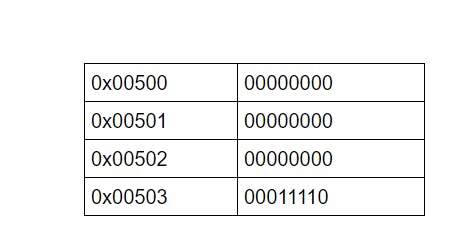
but for general understanding we will consider **scores = [30,40,50,60] ** in below table -
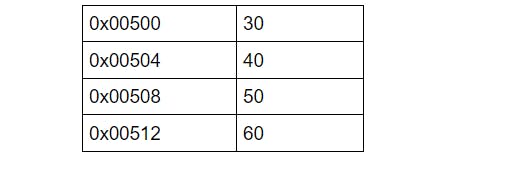
Now taking the above example let's find what will be the result of print(scores[2])
The Indexing starts from 0 hence when scores is assigned the value [30,40,50,60] it is pointing to the memory address at 0th index which is 0x00500
In order to find scores[2] = the initial address + 2 * size of (Integer)
score[2] =0x00500 + 2 * 4
score[2] =0x00508
Adding an element in an array
Assume you want to add 35 at the Index =1
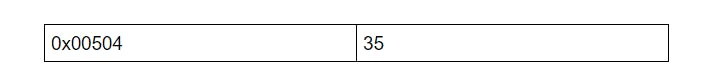
For this, Every element that occurs after the index 1st will be shifted by 1 index and the resulted Array will look like -
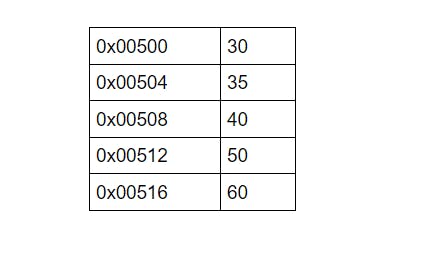
The Big O Time complexity of this will be O(n).
Similarly, we can do deletion in an array and when the element is deleted all the elements shift up by one index.
Python List as a Dynamic Array:
Resizable: Python lists are dynamic, meaning they can grow or shrink in size. When you append an element to a list, if there's enough capacity in the underlying array, the element is simply added. If the capacity is exceeded, Python automatically allocates a new, larger chunk of memory and copies the existing elements into this new memory space.
Efficient: This resizing operation is done in such a way that it provides efficient amortised performance, typically O(1) for append operations, though the worst-case scenario (when resizing occurs) is O(n).
import sys
l = []
for x in range(100):
print(x,sys.getsizeof(l))
l.append(x)
The key points to understand here are the list's dynamic resizing behavior and the use of sys.getsizeof to check the memory size of the list.
Thank-you!
I'm glad you made it to the end of this article. I hope you learned something. If you did, please leave a Like, as it will encourage me in my upcoming write-ups.
Connect with me on Linkedin
Start your own blogs

