What is Sorting?
Sorting refers to the arrangement of the data values in a particular order according to our needs. To perform sorting in any coding language we make use of the sorting algorithms. A sorting algorithm is just a series of orders or instructions. In this, an array is an input, on which the sorting algorithm performs operations to give out a sorted array.
What is Merge Sort?
Just like Quick Sort, Merge Sort is a Divide and Conquer algorithm. It cuts the input array into two parts, calls itself for the two halves, and then merges the two sorted parts together.
Let's see an example to know how the Merger sort works ->
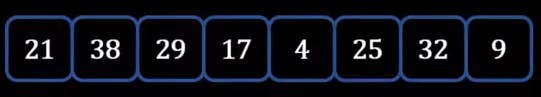
- Assume we have the below list of elements which needs to be sorted using the Merge sort
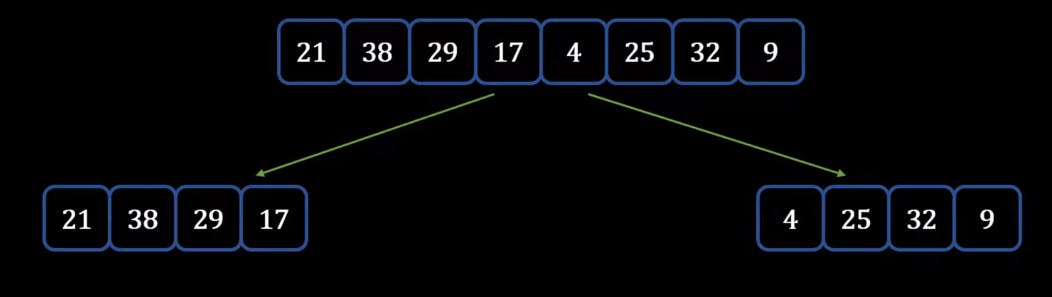
- Now we divide it into two halves, if you have an odd number of elements assume 9 elements then you can divide it into 4 and 5
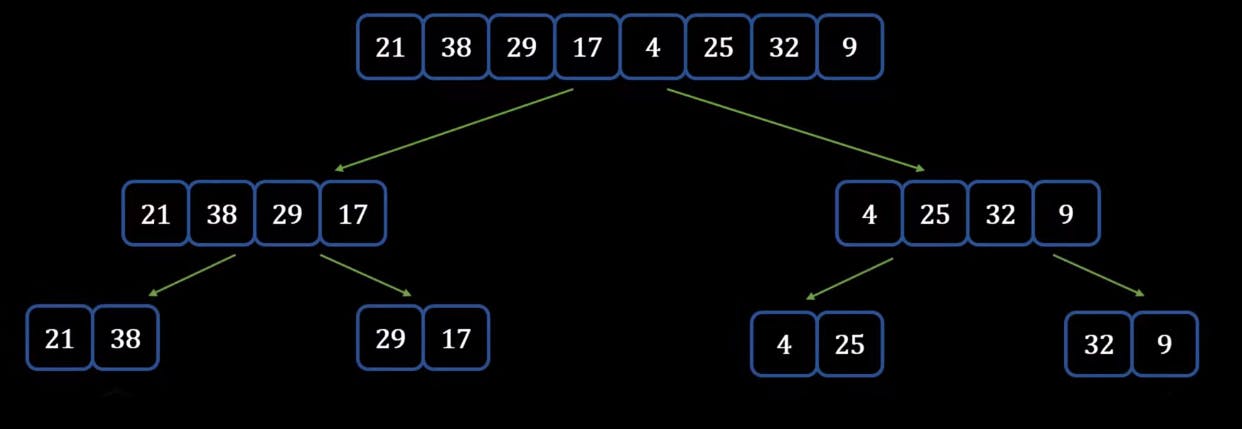
- Now we see that these are not yet ready to be merged back because they are not yet sorted, hence we divide them again into equal halves
- still, we find that few of the elements are not sorted hence we need to divide them again
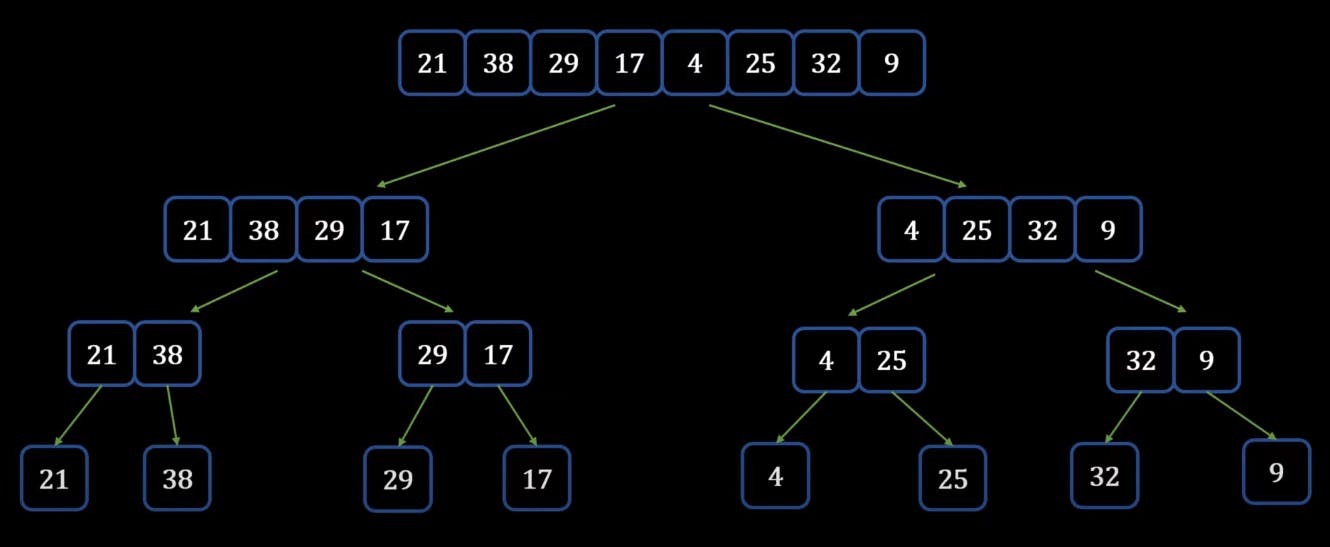
- Now we are left with all the array which have only one element.

- Now from here we need to step back, we will take the first two elements and try to merge them
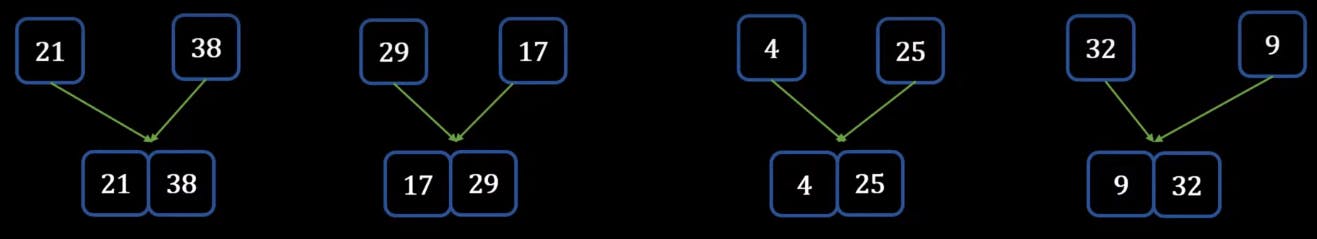
- Once it's done, we can now move to merge the next set of elements
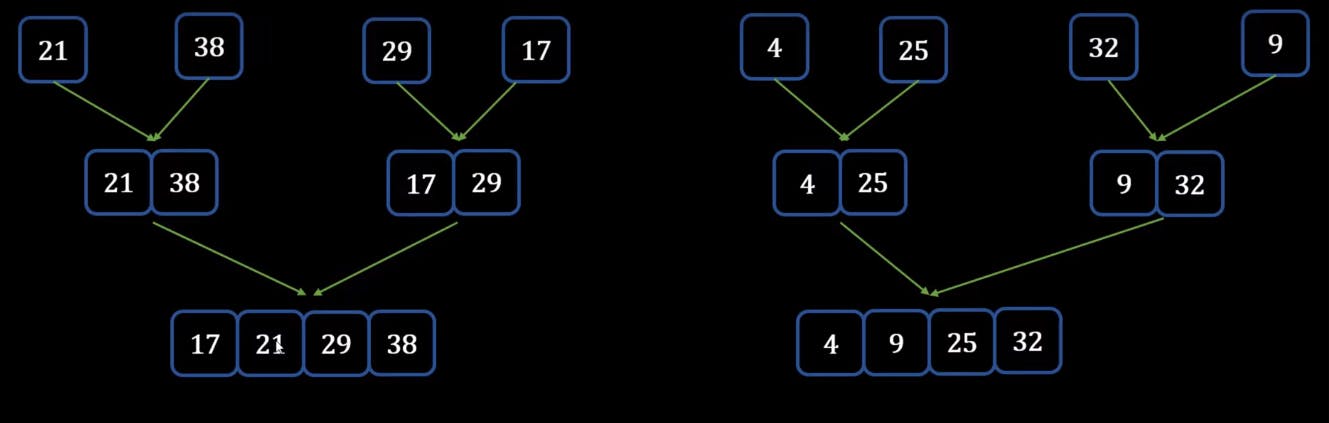
- Finally, we can merger the last two arrays into the single array
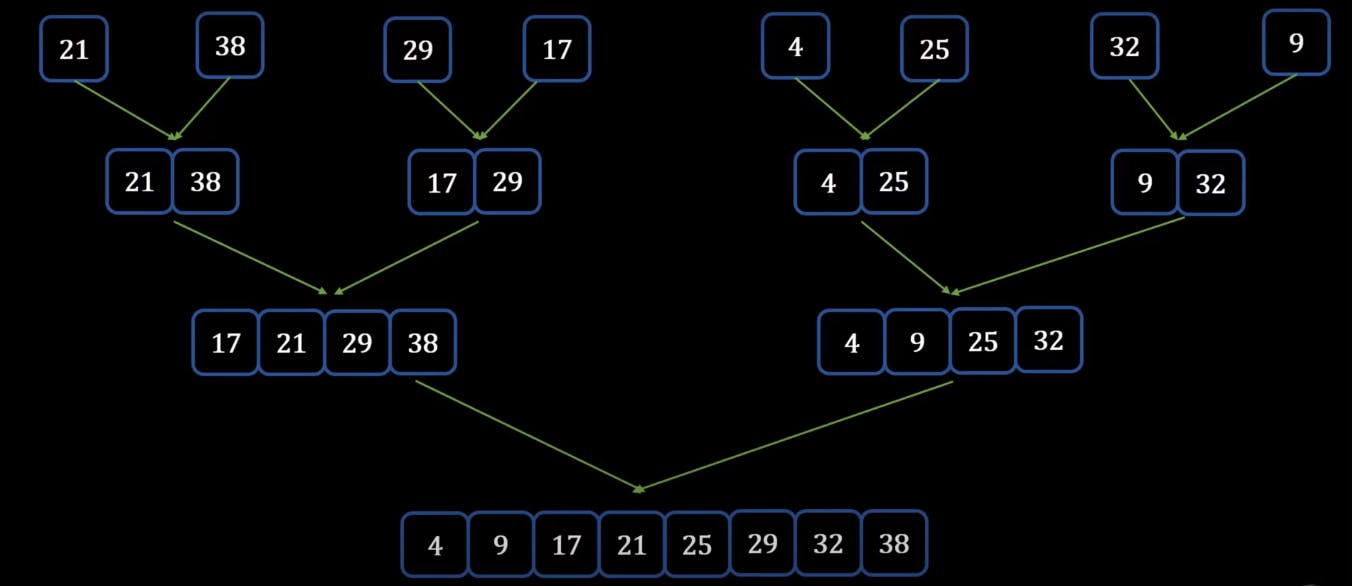
Note -> When you call the built-in SORT function in Python it uses a Hybrid Sort between Merge Sort and Insertion Sort.
Let's Implement using Python
- Let's first define a helper function which will merge the two sorted arrays in one single array or list.
def merge_two_list(array_one,array_two):
sorted_list = []
length_array_one = len(array_one)
length_array_two = len(array_two)
i=j=0
while i<length_array_one and j<length_array_two:
if array_one[i] <= array_two[j]:
sorted_list.append(array_one[i])
i+=1
else:
sorted_list.append(array_two[j])
j+=1
while i<length_array_one:
sorted_list.append(array_one[i])
i+=1
while j<length_array_two:
sorted_list.append(array_two[j])
j+=1
return sorted_list
- Now we will define our Merge sort function which will call itself recursively to split the list in two halves
def merge_sort(mylist):
if len(mylist) <= 1:
return mylist
mid = len(mylist) // 2
left = mylist[:mid]
right = mylist[mid:]
left = merge_sort(left)
right = merge_sort(right)
- let's combine the functions under one single program and add the main function
def merge_two_list(array_one,array_two):
sorted_list = []
length_array_one = len(array_one)
length_array_two = len(array_two)
i=j=0
while i<length_array_one and j<length_array_two:
if array_one[i] <= array_two[j]:
sorted_list.append(array_one[i])
i+=1
else:
sorted_list.append(array_two[j])
j+=1
while i<length_array_one:
sorted_list.append(array_one[i])
i+=1
while j<length_array_two:
sorted_list.append(array_two[j])
j+=1
return sorted_list
def merge_sort(mylist):
if len(mylist) <= 1:
return mylist
mid = len(mylist) // 2
left = mylist[:mid]
right = mylist[mid:]
left = merge_sort(left)
right = merge_sort(right)
return merge_two_list(left,right)
if __name__ == '__main__':
a = [34,5,3,5,34,45,56,67,78,1,2]
print(merge_sort(a))
- We will receive the output as - [1, 2, 3, 5, 5, 34, 34, 45, 56, 67, 78]
Thank-you!
I am glad you made it to the end of this article. I hope you got to learn something, if so please leave a Like which will encourage me for my upcoming write-ups.
- My GitHub Repos
- Connect with me on Linkedin
- Start your own blogs