What do we understand by Sorting in general?
Sorting refers to the arrangement of the data values in a particular order according to our needs. To perform sorting in any coding language we make use of the sorting algorithms. A sorting algorithm is just a series of orders or instructions. In this, an array is an input, on which the sorting algorithm performs operations to give out a sorted array.
What is Quick Sort?
- Quick Sort is a Divide and Conquer algorithm in this we first pick an element as pivot and partitions the given array around the picked pivot. Let's understand this with an example, assume we have the below set of integers -

- Here the first element is 11 and we chose this as a PIVOT.
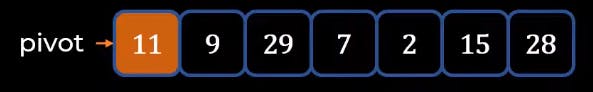
- Now we will try to put Pivot in its right position. In this all the elements left-hand side of 11 are smaller than 11 also all the elements on the right-hand side of 11 should be greater than 11.
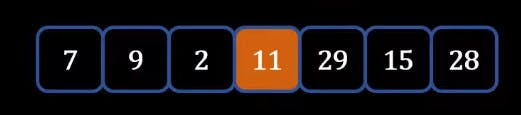
- Now we can mark this 11 sorted and focus on one side. Here in this case we will first ignore the right side and take a look on the left-hand side.

- Now on the left-hand side we will perform the same task, make the first element which is 7 as the PIVOT and then put in the position where the left side of 7 is smaller than it and the right side of 7 is greater than it.


- Now we can see that only single elements are left on both sides of 7 hence. This we can put sorted till 11.

- Now we need to focus on the right side we were left out and perform the same operations there. We will make the first element which is 29 as the PIVOT.

- When we put 29 in its actual position we see that there is no right partition as of now because all the elements left are less than 29

- So again we need to repeat the same process recursively.

- Therefore the elements are sorted using quicksort.

How did we put Pivot in its right position?
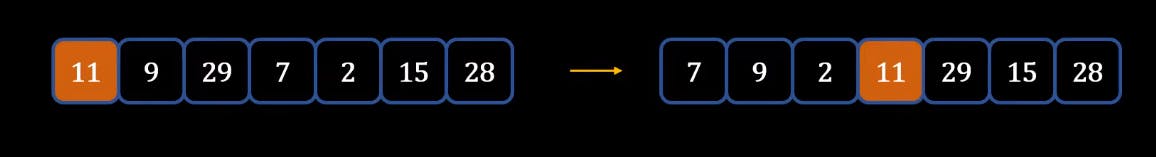
The next question which arises that how to put Pivot in the middle so that all the elements on the left are less than the Pivot and the elements to the right are greater than the Pivot. This process is know as Partitioning.
There are two methods to do that ->
- Hoare Partition
- Lomuto Partition
Hoare Partition
The way that Hoare Partition works is by making two indexes that start at two ends, the two indexes move toward each other until a smaller value on the left side and greater value on the right side is found. When its found those values are swapped and the process is repeated.
let's understand this using the below example
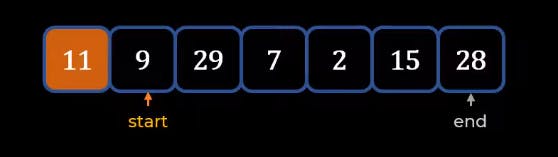
- Here we mark 9 as the start and 28 as the end after making 11 the Pivot. We will start from 9 itself and comparing it will the Pivot which is 11, till we find element greater than the pivot.
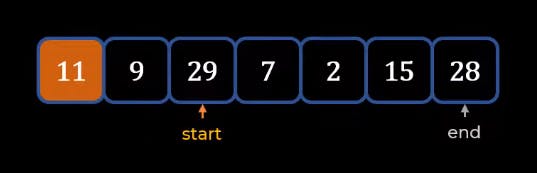
- Once you find an element greater than Pivot just stops at that element. Now we need to focus on the endpoint which is 28, we will move until and unless we find an element less than 11 which is the Pivot.
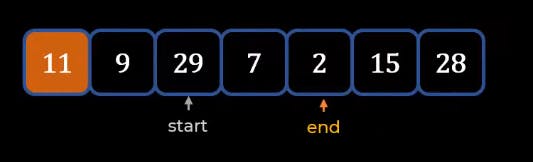
- Now our start = 29 and end = 2, and they have stopped now and then we need to swap their positions.
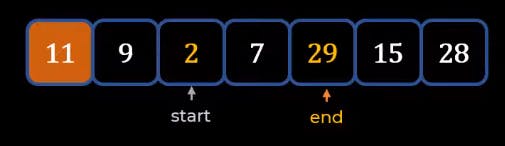
- After swapping we need to again repeat this process until either start is greater than the Pivot or end is less than Pivot and then do the swap. This process goes on to start crosses end. Once you stop swap end and Pivot as we did below
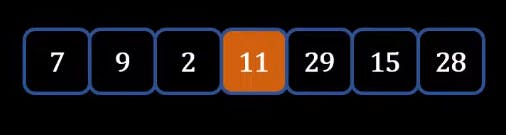
Let's Implement Quicksort (Hoare Partition) using Python
- First, we will see how we want to give the Input by making the main function
if __name__ == '__main__':
mylist = [34,54,23,56,10,20,30,21]
quick_sort(mylist,0,len(mylist)-1)
print(mylist)
- Now we will create a function for doing the quick sort. We can see in the above code how we recursively called quicksort function. we create one more function to do the partitioning.
def quick_sort(mylist,start_index,end_index):
if start_index < end_index:
partition_index = partition(mylist,start_index,end_index)
quick_sort(mylist,start_index,partition_index-1)
quick_sort(mylist,partition_index+1,end_index)
- Now we will make the function for partitioning the list into left and right partition
def partition(mylist,start_index,end_index):
pivot_index = start_index
pivot = mylist[pivot_index]
while start_index < end_index:
while start_index < len(mylist) and mylist[start_index] <= pivot:
start_index += 1
while mylist[end_index]>pivot:
end_index -= 1
if start_index < end_index:
swap(start_index,end_index,mylist)
swap(pivot_index,end_index,mylist)
return end_index
- We are only left with a Swap function
def swap(a,b,arr):
if a != b:
temp = arr[a]
arr[a]=arr[b]
arr[b]=temp
- Let's Sum up all the codes under one complete program.
def swap(a,b,arr):
if a != b:
temp = arr[a]
arr[a]=arr[b]
arr[b]=temp
def partition(mylist,start_index,end_index):
pivot_index = start_index
pivot = mylist[pivot_index]
while start_index < end_index:
while start_index < len(mylist) and mylist[start_index] <= pivot:
start_index += 1
while mylist[end_index]>pivot:
end_index -= 1
if start_index < end_index:
swap(start_index,end_index,mylist)
swap(pivot_index,end_index,mylist)
return end_index
def quick_sort(mylist,start_index,end_index):
if start_index < end_index:
partition_index = partition(mylist,start_index,end_index)
quick_sort(mylist,start_index,partition_index-1)
quick_sort(mylist,partition_index+1,end_index)
if __name__ == '__main__':
mylist = [34,54,23,56,10,20,30,21]
quick_sort(mylist,0,len(mylist)-1)
print(mylist)
- Finally, we are completed with Quicksort using one method for partitioning. There is one more method to perform the partitioning.
Lomuto Partition
- In this case, we decide that the right end element is the Pivot

- The start element which is 11 will be called as P index.
- We keep on moving the P index until we find and element which is greater than Pivot (which is 28)
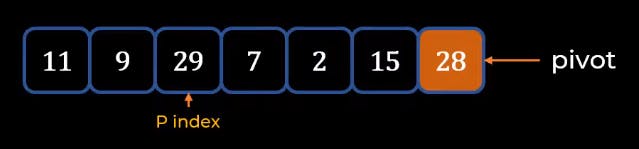
- Then we start a new counter I, and I Index will be the same as the P index.
- The I index will keep on moving until it finds the element less than Pivot (which is 28).
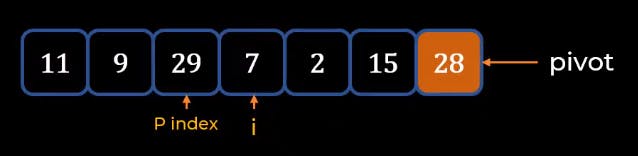
- Now we swap the elements
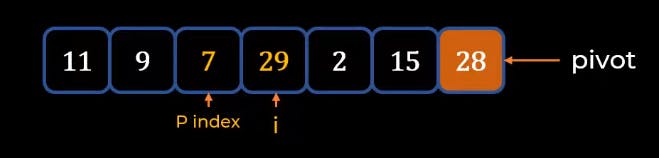
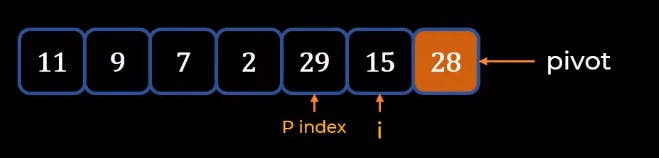
- We again perform the same task, the rule for the P index is that you move P until you find the element which is greater than Pivot whereas in the case of I Index we move I till we find the element less than Pivot.
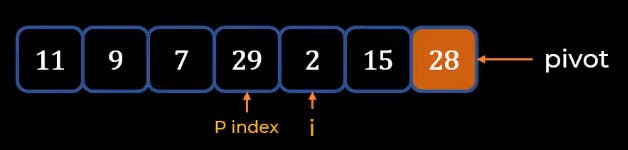 .
.
- Then once we find that element we make a Swap.
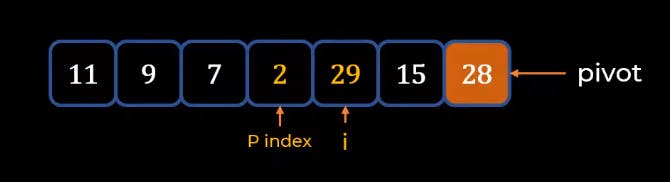
- Once again we perform the same task and swap when we reach the conclusion
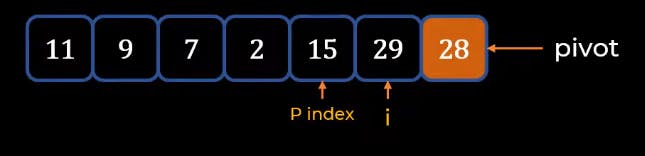
When we finally reach the End we can see that the Pivot which is 28 is now at the right position.
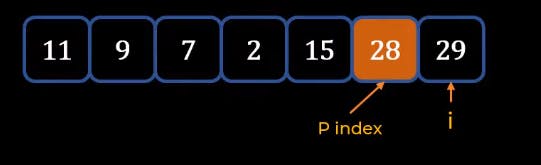
Now you can try giving it a shot by implementing this way of partitioning using python.
Thank-you!
I am glad you made it to the end of this article. I hope you got to learn something, if so please leave a Like which will encourage me for my upcoming write-ups.
- My GitHub Repos
- Connect with me on Linkedin
- Start your own blogs

