What is the issue with Arrays?
Click here to view the article on Arrays
1. Dynamic Size
LinkedList: The size of a LinkedList is dynamic and can grow or shrink as elements are added or removed. There is no need to allocate a fixed amount of memory in advance.
Array: Arrays (Python lists) have a fixed size once created, and though Python’s list dynamically resizes, this involves copying the entire list to a new location, which can be inefficient.
2. Efficient Insertions and Deletions
LinkedList: Insertions and deletions are more efficient, especially for operations at the beginning or middle of the list, since you only need to change the pointers. These operations are O(1)O(1) if the node to insert/delete is already known.
Array: Insertions and deletions in arrays are costly, particularly in the middle or beginning of the array, because elements have to be shifted, leading to O(n)O(n) time complexity.
3. No Wasted Space
LinkedList: Memory allocation is more efficient with LinkedLists as nodes are allocated only as needed. There is no need to allocate a large contiguous block of memory.
Array: Arrays need a contiguous block of memory. Over-allocation of memory often occurs to allow for growth, which can lead to wasted space.
4. No Reallocation
LinkedList: Adding a new element in a LinkedList doesn’t require reallocation of the entire structure. You simply allocate memory for the new node and adjust pointers.
Array: When a Python list grows beyond its current capacity, it needs to reallocate memory to accommodate additional elements, which can be costly.
5. Consistency in Memory Usage
LinkedList: Memory is consistently used, as each element is individually allocated. This can be beneficial in environments where memory usage is fragmented.
Array: Memory usage can be inconsistent due to the need for reallocation when the array grows, potentially leading to temporary spikes in memory usage.
6. Better for Certain Types of Operations
LinkedList: For applications where frequent insertions and deletions are required, especially in the middle of the list, LinkedLists offer better performance.
Array: Arrays are less efficient for operations that require frequently adding or removing elements, especially not at the end of the list.
7. Sequential Access
LinkedList: Sequential access (e.g., iterating over the list) can be more cache-efficient with LinkedLists as nodes are scattered in memory, although this could also be a drawback depending on the context.
Array: Arrays benefit from better cache performance due to their contiguous memory layout, but this advantage disappears if many insertions or deletions are necessary.
What is a Linked List?
A **linked list ** is a linear collection of data elements, in which each element points to the next. The first element contains the address of the second element and the second element contains the address of the third element and so on till the last element contains null. It is a data structure consisting of a collection of nodes that together represent a sequence.
The below image is the pictorial representation of a Linked List.

Insertion in the Linked List
The below image represents a typical insertion in the Linked List
So in case you want to insert 284 at index 1, then this is how it will be done?
All you need to do is change the address pointer at the element 298 - which is currently 0x00A1 (of the second element) to the element that you want to do - which is 0xC702 **( element 284 ) **
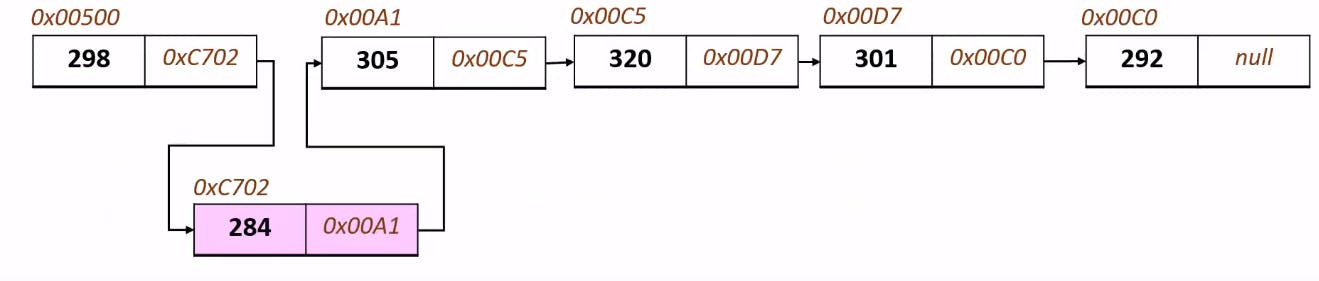
The insertion becomes very easy because now you are just modifying the links unlike arrays in which you had to shift each element by an index.
The Big O complexity for
Inserting Element at the beginning is - O(1)
Deleting Element at the beginning is - O(1)
Inserting/Deleting Element at the end is - O(n) - because you need to traverse through all the elements via their address to reach the end.
Accessing Element by Value - O(n)
What is Doubly Linked List?
A doubly linked list is a linked data structure that consists of a set of sequentially linked records called nodes. Each node contains three fields:
Two link fields(the first contains the address of the previous element and the other contains the address of the next element)
One data field/element field.
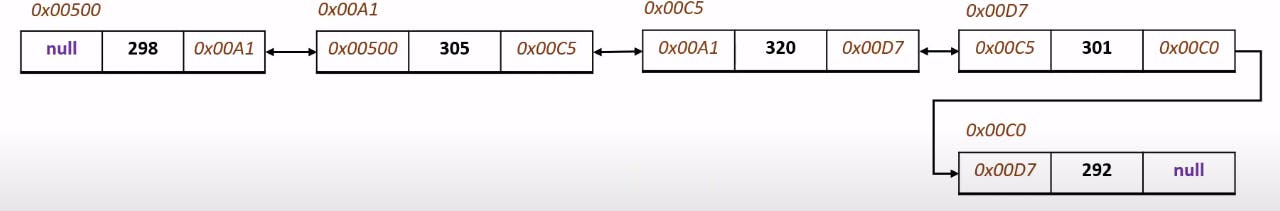
This way the backward traversal becomes very easy.
Let's implement Linked List in Python
- **Creating a class for Node , so we can create or change node functionality whenever we feel like
**
class Node:
#Class for creating a Node which contains the data and the next address
#If this is the first node hence the next value will be none
def __init__(self,data=None,next=None):
self.data = data
self.next = next
- **Creating a class for Linked List to add functions **
class LinkedList:
#Creating a class for LinkedList which contains various functions
def __init__(self):
#head of the Linked List
self.head = None
- **Function for adding an element at the start **
def insert_at_start(self,data):
#Function for inserting at the starting
new_node = Node(data,self.head) #creating a new node
self.head = new_node #now head will point to newly created node
- **Function for inserting an element at the end **
def insert_at_end(self,data):
if self.head is None: #which means there is nothing in the Linked List
new_node = Node(data,self.head) #creating a new node
self.head = new_node #now head will point to newly created node
return
temp = self.head
while temp.next:
temp = temp.next
temp.next = Node(data,None)
- **Function for finding the length of the Linked List **
def find_length(self):
temp = self.head
count = 0
while temp:
count += 1
temp = temp.next
#print(count)
return count
- **Function for deleting element at any index **
def delete_at_index(self,index):
if index < 0 or index >= self.find_length():
raise Exception("Invalid Index")
if index == 0 :
self.head = self.head.next
return
count = 0
temp = self.head
while temp:
if count == index - 1:
temp.next = temp.next.next
break
temp = temp.next
count += 1
- Function for printing the Nodes
def print(self): #funtion for prinitng the nodes and the datas
element = ''
if self.head is None:
element += 'Null'
temp = self.head
while temp: #looping through the head to check the next element
element += str(temp.data)+ '--->'
temp = temp.next
print(element)
- **Main function for creating the Linked List **
if __name__ == '__main__':
ll = LinkedList()
ll.insert_at_start(2)
ll.insert_at_start(3)
ll.insert_at_start(4)
ll.insert_at_end(5)
ll.insert_at_end(9)
ll.find_length()
#ll.delete_at_index(9)
ll.delete_at_index(2)
ll.print()
Well, here is the whole code for you, try running yourself and add new features.
class Node:
#Class for creating a Node which contains the data and the next address
#If this is the first node hence the next value will be none
def __init__(self,data=None,next=None):
self.data = data
self.next = next
class LinkedList:
#Creating a class for LinkedList which contains various functions
def __init__(self):
#head of the Linked List
self.head = None
def insert_at_start(self,data):
#Function for inserting at the starting
new_node = Node(data,self.head) #creating a new node
self.head = new_node #now head will point to newly created node
def insert_at_end(self,data):
if self.head is None: #which means there is nothing in the Linked List
new_node = Node(data,self.head) #creating a new node
self.head = new_node #now head will point to newly created node
return
temp = self.head
while temp.next:
temp = temp.next
temp.next = Node(data,None)
def find_length(self):
temp = self.head
count = 0
while temp:
count += 1
temp = temp.next
#print(count)
return count
def delete_at_index(self,index):
if index < 0 or index >= self.find_length():
raise Exception("Invalid Index")
if index == 0 :
self.head = self.head.next
return
count = 0
temp = self.head
while temp:
if count == index - 1:
temp.next = temp.next.next
break
temp = temp.next
count += 1
def print(self): #funtion for prinitng the nodes and the datas
element = ''
if self.head is None:
element += 'Null'
temp = self.head
while temp: #looping through the head to check the next element
element += str(temp.data)+ '--->'
temp = temp.next
print(element)
if __name__ == '__main__':
ll = LinkedList()
ll.insert_at_start(2)
ll.insert_at_start(3)
ll.insert_at_start(4)
ll.insert_at_end(5)
ll.insert_at_end(9)
ll.find_length()
#ll.delete_at_index(9)
ll.delete_at_index(2)
ll.print()
You Just saw creating a new Linked List using Python and adding some functionality such as Add and Delete. Now you can go ahead and make a few more functions such as inserting at a given index . Even you can try creating a Doubly Linked List.
When not to use LinkedLists:
While LinkedLists offer advantages, it's important to note that they might not always be the best choice. Arrays are generally better when you need:
Random Access: Arrays provide O(1)O(1) time complexity for accessing any element by index, which is not possible with LinkedLists, as they require O(n)O(n) for the same operation.
Low Memory Overhead: LinkedLists have a higher memory overhead because they require additional storage for pointers.
Thank-you!
I am glad you made it to the end of this article. I hope you got to learn something, if so please leave a Like which will encourage me for my upcoming write-ups.
Connect with me on Linkedin
Start your own blogs

