Before we start, I would like you to go through the below articles which will give a brief introduction to the Database and its management.
Create, Read, Update, and Delete (CRUD) are the four basic functions that models should be able to do, at most.
Basic Data Types
An SQL developer must decide what type of data will be stored inside each column when creating a table. In MySQL, there are three main data types: string, numeric, and date and time.
- INT -> Any Whole Number
- DECIMAL(M, N) -> Decimal values are store in the form of M being before and N after the Decimal
- VARCHAR(l) ->String of text length l
- BLOB -> Binary Large Objects, these store large data
- DATE -> Stores Date in the format YYYY-MM-DD
- TIMESTAMP -> Stores Time frames in the format YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS
These are not all the datatypes, just the basic once to help you get started.
How to create a Table?
- First, we need to install the MYSQL Community server and set that up. You can use the MYSQL Command Line Client , here I am using a text editor which is POP SQL .
- You can create a database with the command CREATE DATABASE RANDOM; where I gave RANDOM as my database name.
- In Order to Create a table -> CREATE TABLE student (); (where CREATE and TABLE are two SQL reserved words)
- Now we need to defile different columns which should be added between the parenthesis of the student () as we have mentioned below.
CREATE TABLE student (
student_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(25),
subject VARCHAR(25)
);
DESCRIBE student;
- we can use the DESCRIBE statement to show the table. After this, we can run the above code.
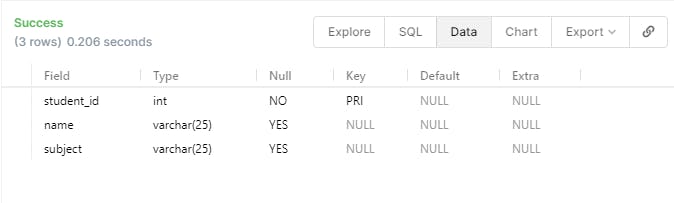
- Now in order to delete this table we can use the command DROP TABLE student
- We can use the ALTER TABLE statement to add in a new column.
ALTER TABLE student ADD cgpa DECIMAL(2,1);
DESCRIBE student;
- We will get the output as
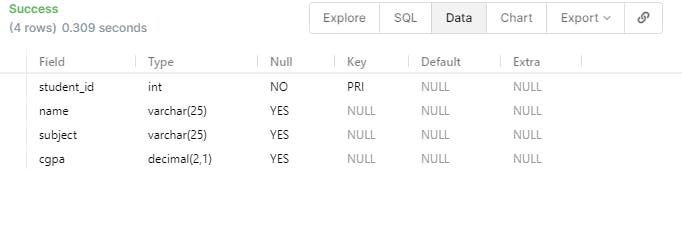
- We can also Drop the added column using the command ALTER TABLE student DROP COLUMN cgpa
How to Insert in a Table?
- In order to insert the objects into the TABLE we will use the command INSERT INTO table_name VALUES(insert values in the same sequence as mentioned while creating a table)
INSERT INTO student VALUES(
5,'Akshat','Computers'
);
SELECT * FROM student;
- In order to get all the information from the TABLE we will make use of the command SELECT * FROM student; As you can see below I have added 5 people to the table.
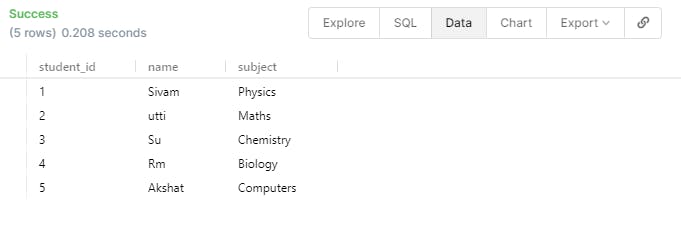
- What if we don't know the exact subject of that student then we can mention as below
INSERT INTO student(student_id,name) VALUES(
6,'Tsri'
);
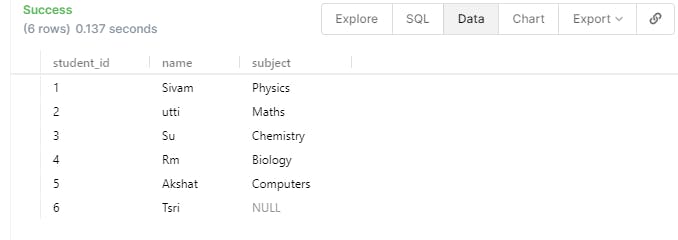
You might get an error if you try inserting an object with a pre-existing Primary Key because Primary Keys should be unique for each Student (Object)
- If you want to set a few rules for your TABLE you can do that, Imaging you want your NAME filed not to be null and the SUBJECT filed to be UNIQUE. This can be done by using the below statement. They KEYWORDS -> UNIQUE and SUBJECT are known as constraints.
CREATE TABLE student(
student_id INT,
name VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
subject VARCHAR(20) UNIQUE,
PRIMARY KEY(student_id)
);
- If you want to give a DEFAULT value to any of the objects. We can use the below statement to do that.
CREATE TABLE student(
student_id INT,
name VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
subject VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT 'undecided',
PRIMARY KEY(student_id)
);
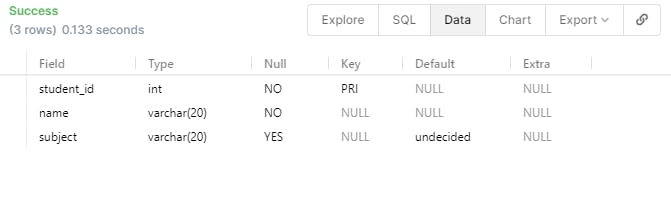
you need to DROP the table again and again if you are recreating it
- What if you want to automatically Increment the ID Value of the student every time when you add a new student to the list. This can be done using the keyword AUTO_INCREMENT. Also, we will go ahead and insert the Students without the ID.
CREATE TABLE student(
student_id INT AUTO_INCREMENT,
name VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
subject VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT 'undecided',
PRIMARY KEY(student_id)
);
INSERT INTO student(name,subject) VALUES('Akshat','Computers');
INSERT INTO student(name,subject) VALUES('Sivam','Physics');
INSERT INTO student(name,subject) VALUES('Utti','Maths');
INSERT INTO student(name,subject) VALUES('Su','Chemistry');
INSERT INTO student(name) VALUES('Tsri');
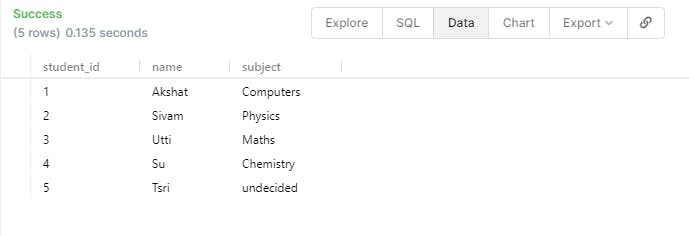
How to Update and Delete in a table?
- If you want to UPDATE the subject of any student then we can use the UPDATE statement and the WHERE condition as below.
UPDATE student
SET subject='Biology'
WHERE name ='Sivam';
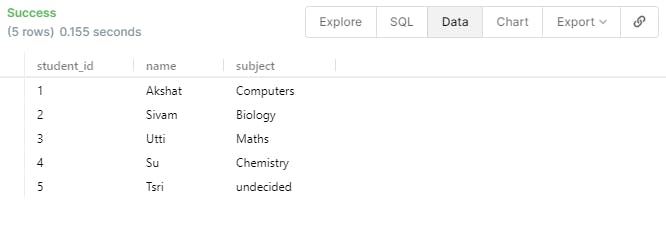
- We can play around with this a little, what if we want to change the Subject Computers and Maths to CompMaths. We can use the below statement.
UPDATE student
SET subject='Compmaths'
WHERE subject = 'Maths' or subject = 'Computers';
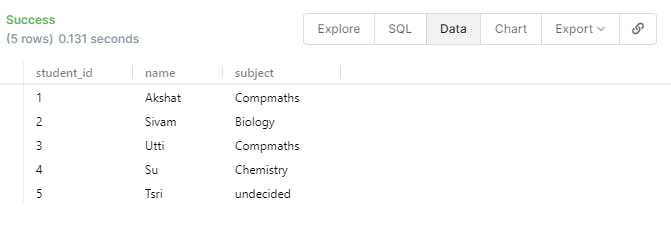
- What if we need to edit or change the NAME of a student and also it's subject. You can issue the below statement.
UPDATE student
SET name='Aks' , subject ='Data'
WHERE student_id = 1;
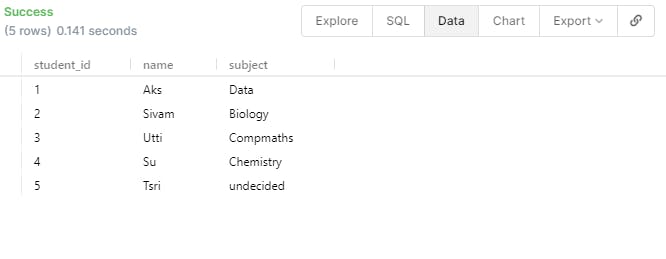
- If you want to DELETE all of the rows inside the table you can use the below statement.
DELETE FROM student;
- If you want to DELETE some data specifically like you want to delete the student with ID = 5 because he might have left the school then you can use the below statement.
DELETE FROM student
WHERE student_id = 5;
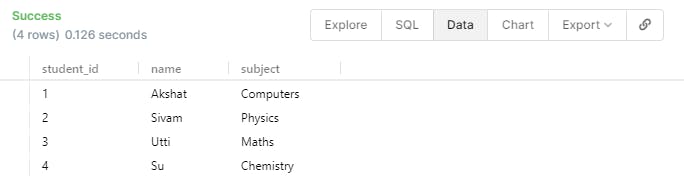
Basic Queries
- We have already seen the keyword SELECT that is being used to get or extract the exact information from the Database itself. So far we are using the '*' which means that we want all the information from that particular table. We can either select specific information instead of all the information.
- If we want to only get the names of all the student we can use the statement as below.
SELECT name FROM student;
or
SELECT student.name , student.subject FROM student;
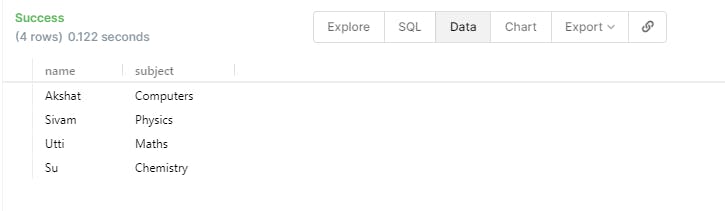
- We can also ORDER the above information by using the below statement.
SELECT student.name , student.subject FROM student ORDER BY student.name;
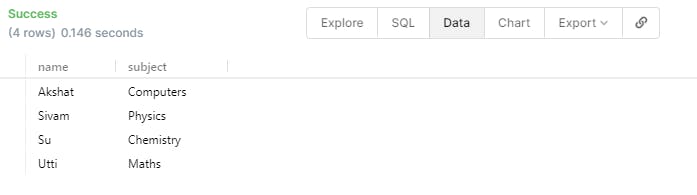
- You can also LIMIT the number of results that we are getting.
SELECT student.name , student.subject FROM student ORDER BY student.name LIMIT 2 ;
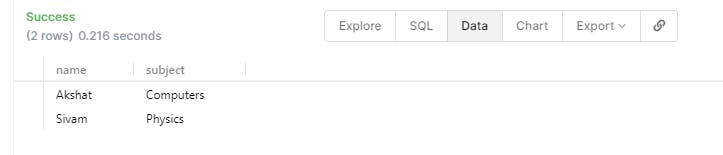
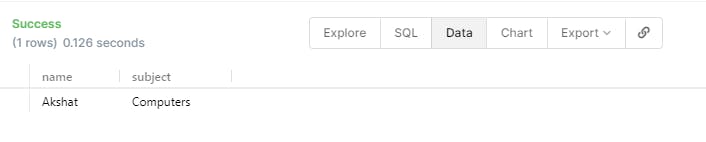
- We can also filter these results using the keyword WHRER as we did while we were updating the student table. We can now only get the students who have the subject as Computers.
SELECT student.name , student.subject FROM student WHERE subject='Computers';
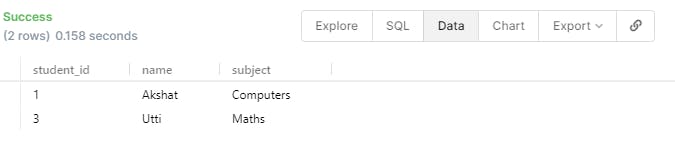
- There is an IN keyword that will let us find the information which belongs to a list of items mentioned.
SELECT * FROM student WHERE name IN ('Akshat','Utti') ;
Important comparison operators ->
- -- -> Anything after this will be a comment
- < -> Less than
- > -> Greater than
- <= -> Less than or Equal to
- >= -> Greater than or Equla to
- =-> Equal to
- <> -> Not equal to
- AND -> And operator
- OR-> Or operator
Thank-you!
I am glad you made it to the end of this article. I hope you got to learn something, if so please leave a Like which will encourage me for my upcoming write-ups.
- My GitHub Repos
- Connect with me on Linkedin
- Start your own blogs

