PermalinkWhat is a Relational Database Management System?
The relationship between the data is defined in the form of tables. A relational database is one of the most famous types of DBMS. RDBMS or relational database management system helps the user create and maintain a relational database
Structured Query Language or SQL ->It is a standardized language for interacting with RDBMS. Used to perform the C.R.U.D Operations (Create, Read, Update, Delete) also they are used to define tables and structures. We can use SQL to create, retrieve, update and delete data.
SQL is a Hybrid language, it is a combination of four different languages ->
- Data Query Language (DQL) -> used to query the database for information - Data Definition Language (DDL) -> used to define the database schemas
- Data Control Language (DCL) -> user and permission management
- Data Manipulation Language (DML) -> used for inserting, updating and deleting data from the database
PermalinkWhat are Queries?
They are request made to the database management system for specific information, as the database's structure becomes more and more complex it becomes difficult to get the specific piece of information form the database.
PermalinkKeys
Keys help you to identify any row of data in a table. In a real-world application, a table could contain thousands of records. Moreover, the records could be duplicated. Keys ensure that you can uniquely identify a table record despite these challenges.
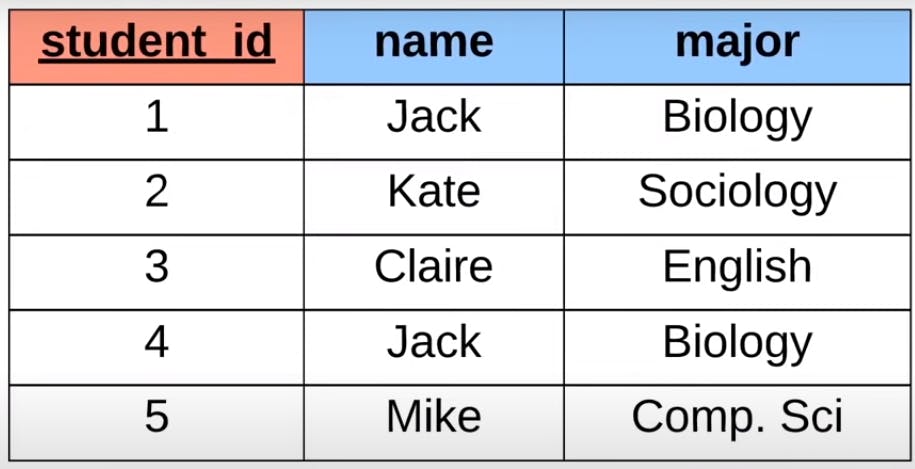
Above we can see the example of a student table. In the above table, we have 3 main pieces of information stored the student ID, name and the subject/major which are the attributes of the student table.
Primary Key ->The PRIMARY KEY constraint uniquely identifies each record in a table. It must contain UNIQUE values, and cannot contain NULL values. A table can have only ONE primary key; and in the table, this primary key can consist of single or multiple columns. This primary key can be anything, this could be a string or a number.
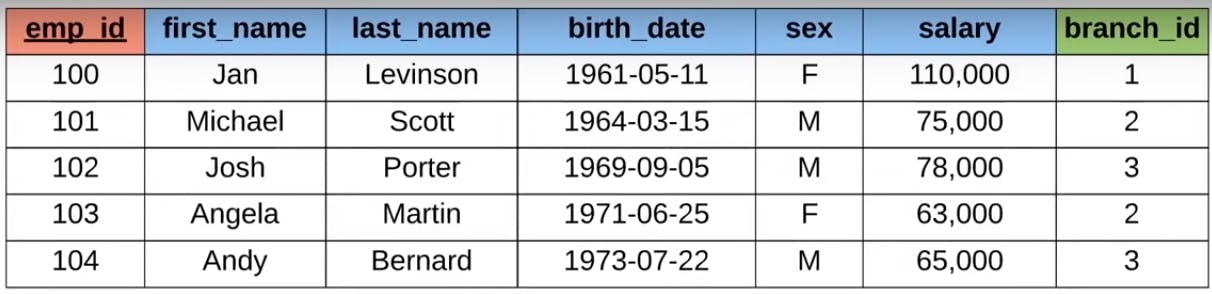
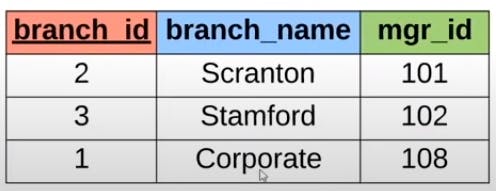
- Foreign Key -> A FOREIGN KEY is a key used to link two tables together. It is a field (or collection of fields) in one table that refers to the PRIMARY KEY in another table. The table containing the foreign key is called the child table, and the table containing the candidate key is called the referenced or parent table. In the below example the branch_id is a foreign key
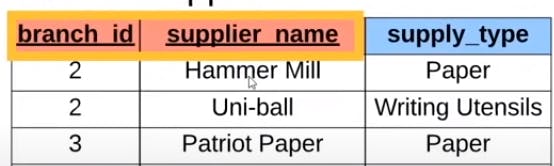
- Composite Key -> This is also known as Compound Key. It is a combination of more than one fields/columns of a table. It can be a Candidate key, Primary key. For example, in the below example we have branch_id and supplier_name work as a compound key.
- Super Key -> A super key is a group of single or multiple keys which identifies rows in a table
- Candidate Key -> it's a set of attributes that uniquely identify tuples in a table. Candidate Key is a super key with no repeated attributes.
- Alternate Key -> It is a column or group in a table that uniquely identify every row in that table. A table can have multiple choices for a primary key but the only one can be set as the primary key. All the keys which are not primary key are called an Alternate Key.
PermalinkThank-you!
I am glad you made it to the end of this article. I hope you got to learn something, if so please leave a Like which will encourage me for my upcoming write-ups.
- My GitHub Repos
- Connect with me on Linkedin
- Start your own blogs
Subscribe to our newsletter
Read articles from Carbon Coffee directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.

