What is a Graph?
A Graph is a non-linear data structure consisting of nodes and edges. The nodes are sometimes also referred to as vertices and the edges are lines or arcs that connect any two nodes in the graph.
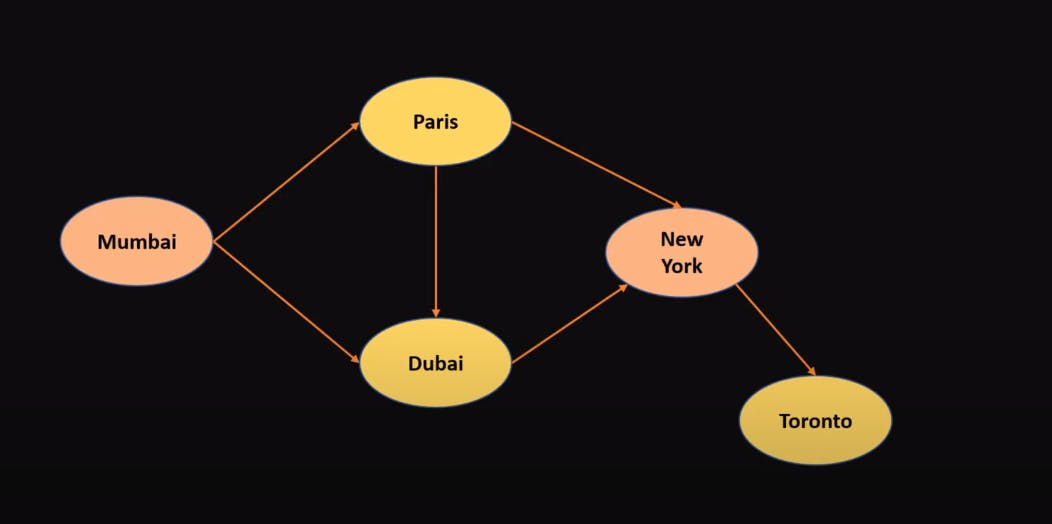
How is a Graph different from a Tree ?
A Tree should have one path between two nodes, whereas in the case of a Graph it is a complex data structures where we can randomly connect any two nodes, as we see in the above graph.
What are the Types of Graph?
Weighted Graph -> It is a type of Graph whose edges have values marked. These values are known as weights or cost or length. These values might represent the distance between two points or the bandwidth.
Unweighted Graph -> Yes you are correct, there is no value or weight associated with the edge.
- Undirected Graph -> the edges are bidirectional which means that there is no direction associated with them. Hence, the graph can be traversed in either direction.
- Directed Graphs -> This Graph is sometimes referred to as the Diagraph. This is a set of vertices (nodes) connected by edges, with each node having a direction associated with it. Edges are usually represented by arrows pointing in the direction the graph can be traversed.
Let's Implement Graph using Python
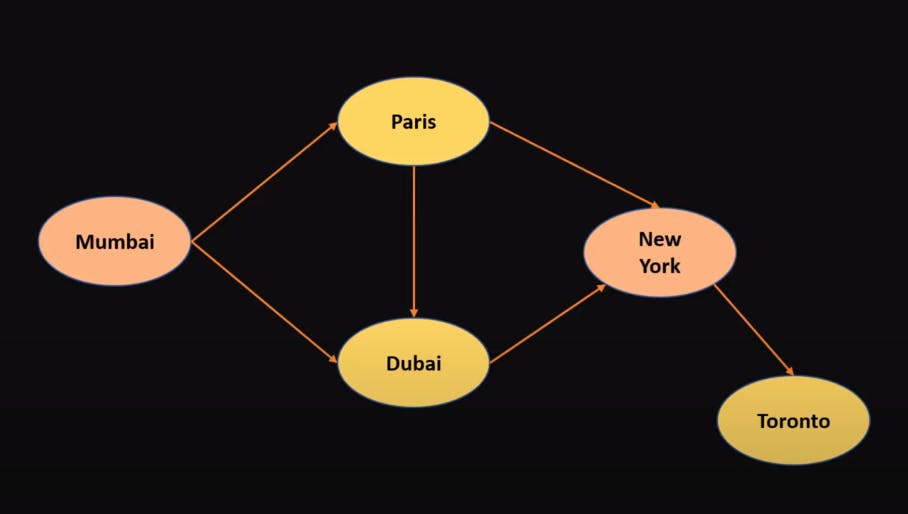
- One way of implementing this Graph in Python is using a Tuple. We will be using the below Graph and try to Implement it.
class Graph:
def __init__(self,edges):
self.edges = edges
if __name__ == '__main__':
routes = [
("Mumbai","Paris")
("Mumbai","Dubai")
("Paris","Dubai")
("Paris","New York")
("Dubai","New York")
("New York","Toronto")
]
route_graph = Graph(routes)
- The first thing that we will use is to transform from the above Tuple to this a better Data Structure which is a Dictionary.
def __init__(self,edges):
self.edges = edges
self.graph_dict = {}
for start,end in self.edges:
if start in self.graph_dict:
self.graph_dict[start].append(end)
else:
self.graph_dict[start]=[end]
print(self.graph_dict)
- Now we need to add a function to get the paths.
def get_paths(self,start,end,path=[]):
self.path = path
path = path + [start]
if start == end :
return path
if start not in self.graph_dict:
return []
paths=[]
for node in self.graph_dict[start]:
if node not in path :
new_path = self.get_paths(node,end,path)
for p in new_path:
paths.append(p)
return paths
- We have to add a feature for getting the shortest path between the two cities.
def get_short_path(self,start,end,path=[]):
path = path + [start]
if start not in self.graph_dict:
return None
if start==end:
return path
short_path = None
for node in self.graph_dict[start]:
if node not in path:
sp = self.get_short_path(node,end,path)
if sp:
if short_path is None or len(sp) < len(short_path):
short_path = sp
return short_path
- Let's Sum up all the codes under one program and add the main function
class Graph:
def __init__(self,edges):
self.edges = edges
self.graph_dict = {}
for start,end in self.edges:
if start in self.graph_dict:
self.graph_dict[start].append(end)
else:
self.graph_dict[start]=[end]
print(self.graph_dict)
def get_paths(self,start,end,path=[]):
self.path = path
path = path + [start]
if start == end :
return path
if start not in self.graph_dict:
return []
paths=[]
for node in self.graph_dict[start]:
if node not in path :
new_path = self.get_paths(node,end,path)
for p in new_path:
paths.append(p)
return paths
def get_short_path(self,start,end,path=[]):
path = path + [start]
if start not in self.graph_dict:
return None
if start==end:
return path
short_path = None
for node in self.graph_dict[start]:
if node not in path:
sp = self.get_short_path(node,end,path)
if sp:
if short_path is None or len(sp) < len(short_path):
short_path = sp
return short_path
if __name__ == '__main__':
routes = [
("Mumbai","Paris"),
("Mumbai","Dubai"),
("Paris","Dubai"),
("Paris","New York"),
("Dubai","New York"),
("New York","Toronto")
]
route_graph = Graph(routes)
start = 'Mumbai'
end = 'New York'
print(route_graph.get_paths(start,end))
print(route_graph.get_short_path(start,end))
- Now your Graph Function is completed, try adding more functions according to your needs
Thank-you!
I am glad you made it to the end of this article. I hope you got to learn something, if so please leave a Like which will encourage me for my upcoming write-ups.
- My GitHub Repos
- Connect with me on Linkedin
- Start your own blogs

