What do we understand by Sorting in general?
Sorting refers to the arrangement of the data values in a particular order according to our needs. To perform sorting in any coding language we make use of the sorting algorithms. A sorting algorithm is just a series of orders or instructions. In this, an array is an input, on which the sorting algorithm performs operations to give out a sorted array.
About Bubble Sort :
- Bubble sort is one of the sorting algorithms that we discussed above. It is also known as Sinking sort sometimes.
- Is a simple sorting algorithm that repeatedly steps through the list, compares adjacent elements and swaps them if they are in the wrong order. The pass of the list is repeated until the list is sorted.
- As we can see in the below example. we have a list that needs to be sorted : [38,9,29,72,15,28]

- Now we will start from the 0th index and compare it with the next adjacent element.
- If the Number is smaller then we will swap it else will move to the next element.
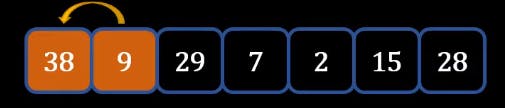
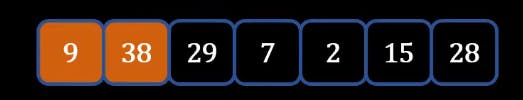
- Similarly, we will proceed.
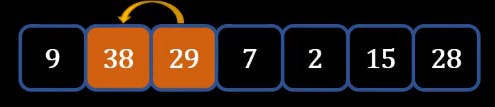
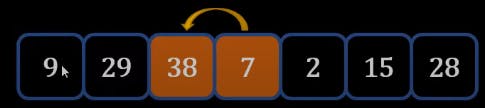
- At the end of the first loop we will get a list like this

- As a result, we can see that 38 which was the highest number is sent to the most right.
- Now we will need to again go through the list comparing the elements from the very beginning also we can now ignore 38 which is already at a sorted position.
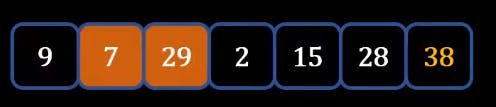
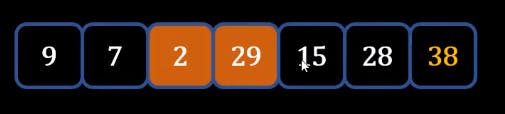
- Now after the second Iteration you will get the following list where 29 and 38 will be fixed because they are sorted.

- we need to keep performing this till we reach the first element so that our final list is sorted.
Let's Implement this in Python
- First, we will define the function which will implement the Bubble sort.
def bubble_sort(mylist):
size = len(mylist)
for k in range(size-1):
for i in range (size-1-k):
if mylist[i]>mylist[i+1]:
temp = mylist[i]
mylist[i] = mylist[i+1]
mylist[i+1]=temp
return mylist
- Now let's add the main function and try to run it
def bubble_sort(mylist):
size = len(mylist)
for k in range(size-1):
for i in range (size-1-k):
if mylist[i]>mylist[i+1]:
temp = mylist[i]
mylist[i] = mylist[i+1]
mylist[i+1]=temp
return mylist
if __name__ =='__main__':
mylist = [3,5,1,2,3,89,0,4,34]
print(bubble_sort(mylist))
#output is [0, 1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5, 34, 89]
- One more thing that we need to keep in mind that, if in any case, the user sends in a sorted list then we don't want our code to run through the whole loop and then figure out that it was sorted.
- Simply we can check that. If after the first iteration there were no swaps made which means that the list that was provided as an Input was already sorted and we can break through it.
- For this we will make use of the variable Swap which will be initially set to False, if the loops swaps the element so the Swap variable will be set to True else will remain false.
def bubble_sort(mylist):
size = len(mylist)
for k in range(size-1):
swapped = False
for i in range (size-1-k):
if mylist[i]>mylist[i+1]:
temp = mylist[i]
mylist[i] = mylist[i+1]
mylist[i+1]=temp
swapped = True #this will tell us that if there was no swap then the list is already sorted
if not swapped:
break
return mylist
if __name__ =='__main__':
mylist = [3,5,1,2,3,89,0,4,34]
#mylist = [0, 1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5, 34, 89]
print(bubble_sort(mylist))
#output is [0, 1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5, 34, 89]
- You can actually Debug this code and check how this is more efficient as compared to the above code, try giving in a sorted element list.
Thank-you!
I am glad you made it to the end of this article. I hope you got to learn something, if so please leave a Like which will encourage me for my upcoming write-ups.
- My GitHub Repos
- Connect with me on Linkedin
- Start your own blogs

