What do you understand by Searching?
Searching is the process of finding a given value position in a list of values. We can also say that It is the algorithmic process of finding a particular item in a collection of items.
Linear Search VS Binary Search ->
- A linear search is also known as a sequential search that simply scans each element at a time. Suppose we want to search an element in an array or list; we simply calculate its length and do not jump at any item.
- Below it the function to implement a Linear Search using Python. We can simply see that there is a for loop and we are checking for the value X in the loop. Hence the complexity for this will be O(n) .
def linear_search(mylist,searching_for):
for index,element in enumerate(mylist):
if element == searching_for:
return index
return -1
if __name__ == '__main__':
mylist = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
searching_for = 5
print(f"The Element is present at the Index {linear_search(mylist,searching_for)} ")
- A Binary Search is a search in which the middle element is calculated to check whether it is smaller or larger than the element which is to be searched. The main advantage of using binary search is that it does not scan each element in the list. Instead of scanning each element, it performs the searching to the half of the list. So, the binary search takes less time to search an element as compared to a linear search.
- Like in the below example we are searching for 32 from the list.
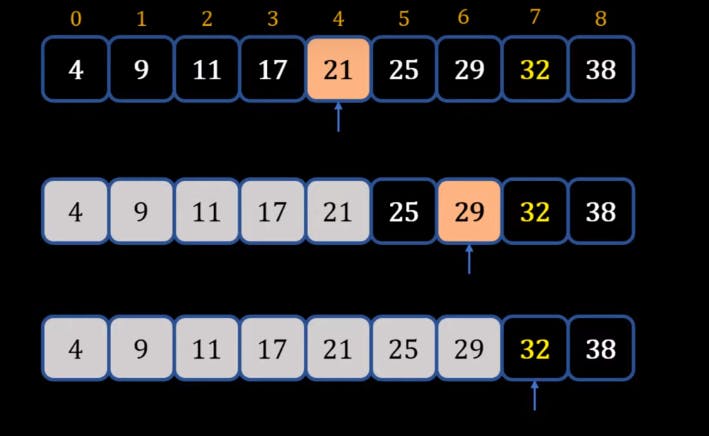
- The Time Complexity for Binary Search is O (log(n)).
Let's Implement Binary Search in Python.
- First, we will define the main function from where we can invoke the Binary Search Function. One thing to keep in mind that we will need the list to be sorted else the Search won't work.
if __name__ == '__main__' :
mylist = [12,23,34,45,55,56,78,89,90]
value = 55
myfunc = binary_search(mylist,value)
print(f"The value = {value} is present at the Index = {myfunc}")
- Now we will define the main function.
def binary_search(mylist,value):
left_index = 0
right_index = len(mylist) - 1
while left_index <= right_index :
mid_index = (left_index + right_index) // 2
mid_number = mylist[mid_index]
if mid_number == value:
return mid_index
if mid_number < value :
left_index = mid_index + 1
else:
right_index = mid_index -1
return None
- We can also add a function to implement the same Binary search using the Recursion
def binary_search_rec(mylist,value,left_index,right_index):
if right_index < left_index:
return None
mid_index = (left_index + right_index) // 2
mid_number = mylist[mid_index]
if mid_number == value:
return mid_index
if mid_number < value :
left_index = mid_index + 1
else:
right_index = mid_index -1
return binary_search_rec(mylist,value,left_index,right_index)
- let's sum up the code under one single program
def binary_search(mylist,value):
left_index = 0
right_index = len(mylist) - 1
while left_index <= right_index :
mid_index = (left_index + right_index) // 2
mid_number = mylist[mid_index]
if mid_number == value:
return mid_index
if mid_number < value :
left_index = mid_index + 1
else:
right_index = mid_index -1
return None
def binary_search_rec(mylist,value,left_index,right_index):
if right_index < left_index:
return None
mid_index = (left_index + right_index) // 2
mid_number = mylist[mid_index]
if mid_number == value:
return mid_index
if mid_number < value :
left_index = mid_index + 1
else:
right_index = mid_index -1
return binary_search_rec(mylist,value,left_index,right_index)
if __name__ == '__main__' :
mylist = [12,23,34,45,55,56,78,89,90]
value = 89
myfunc = binary_search(mylist,value)
recfunc = binary_search_rec(mylist,value,0,8)
print(f"The value = {value} is present at the Index = {myfunc}")
print(f"The value = {value} is present at the Index = {recfunc}")
Thank-you!
I am glad you made it to the end of this article. I hope you got to learn something, if so please leave a Like which will encourage me for my upcoming write-ups.
- My GitHub Repos
- Connect with me on Linkedin
- Start your own blogs

